Staking is the process of locking up your cryptocurrency in a blockchain network to help secure and operate it. In return, you earn rewards, usually paid in the same cryptocurrency. It is a core feature of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains such as Solana, Cardano, and Ethereum. Instead of relying on energy-heavy mining, PoS networks use staked tokens to validate and confirm transactions.
Why is staking more beneficial than normal crypto investing?
With staking, you can earn passive income in the form of rewards (similar to interest rates) while still holding your tokens. Many platforms even auto-compound rewards, allowing your holdings to grow faster over time. By staking, you also support and strengthen the blockchain community, since your tokens help secure the network. However, there are trade-offs—funds may be locked for a period, and staking rewards don’t protect you from price drops in the token itself.
What can you stake?
- Cryptocurrencies on PoS blockchains (e.g., ETH, SOL, ADA).
- NFTs (in some DeFi ecosystems).
- Liquidity pool (LP) tokens earned from providing liquidity in DeFi.
- Stablecoins (USDC, DAI, etc.) for more stable but lower returns.
What tools do you need to stake?
If you’re new to staking, you don’t need advanced technical skills. To begin, you’ll need:
- A crypto wallet such as MetaMask, Phantom, or Ledger.
- An internet connection and tokens that support staking.
You can also use staking platforms—many centralized exchanges like Coinbase and Binance have simple one-click staking options. For more advanced users, running a validator node is also possible.
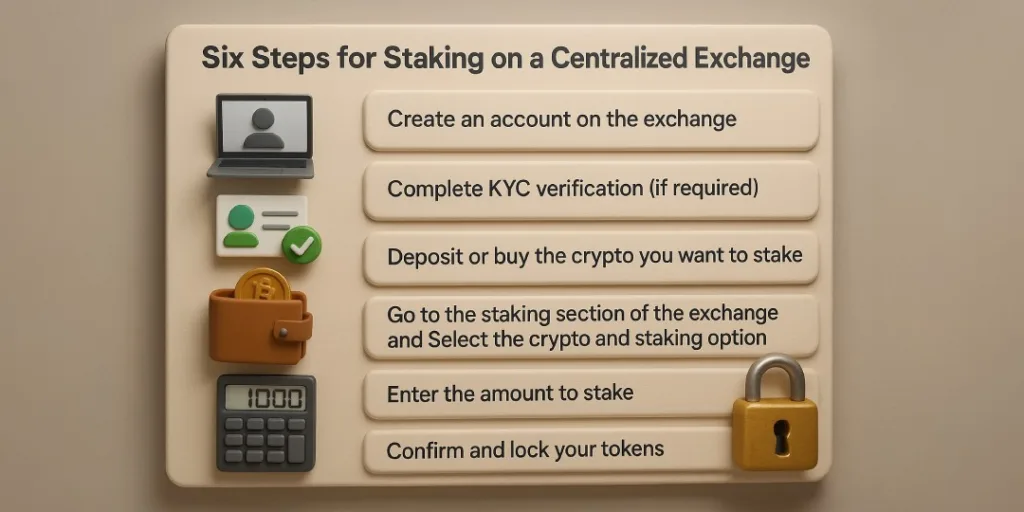
A closer look at validator nodes
Validator nodes are computers that run blockchain software and verify new transactions. They are the backbone of Proof-of-Stake networks, ensuring the blockchain remains secure and decentralized. Running your own validator gives you the highest level of control and reward potential, but it comes with significant requirements:
- A large minimum stake (e.g., 32 ETH on Ethereum).
- Strong technical knowledge to manage the node and keep it online.
- Reliable internet and hardware setup.
For most beginners, it’s easier to delegate their tokens to an existing validator instead of running one themselves.
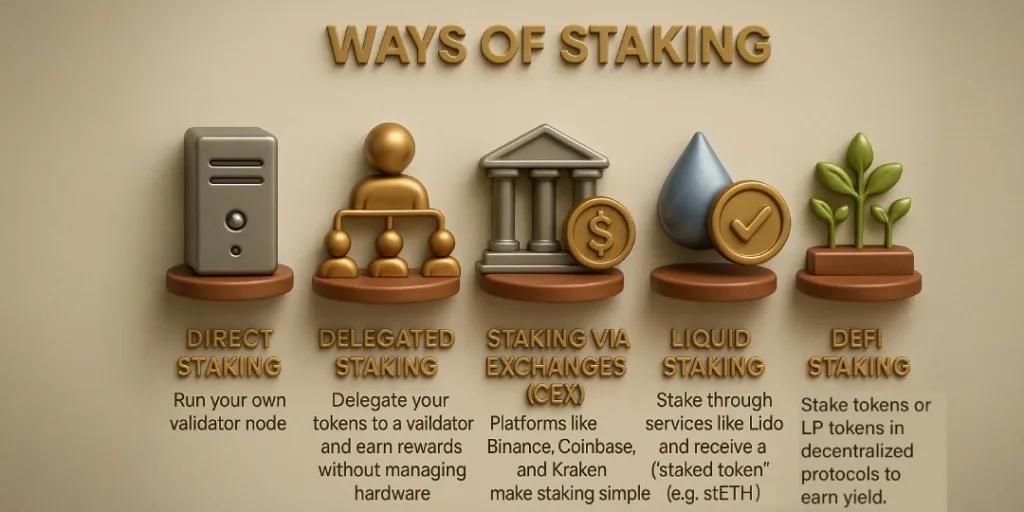
Are there companies that offer staking, and what are the benefits?
Yes, companies and platforms like Lido, Rocket Pool, Coinbase, and Binance offer staking services.
Benefits if they do it for you:
- No technical expertise required.
- Lower entry barrier (you can stake small amounts).
- Some offer liquidity through staked tokens.
Drawbacks:
- They take a cut of your rewards.
- You don’t control your private keys if using centralized services.
Is staking safe?
Staking is generally considered safer than trading, but risks remain:
- Price risk: The value of your staked coins may drop.
- Slashing risk: Validators can be penalized (slashed) for being offline or malicious, which may result in reduced rewards.
- Platform risk: If you stake through an exchange or DeFi protocol, there’s always a chance of hacks, bugs, or insolvency.
FAQs
Can I unstake at any time?
Depends on the blockchain:
Ethereum: ~2–5 days wait time.
Solana: ~2–3 days.
Some DeFi platforms: instant, some lock your tokens for weeks.
What happens if I don’t stake?
Nothing bad, your coins just sit idle. But compared to stakers, you’re missing out on extra rewards
Do I get paid in dollars or crypto?
Rewards are almost always paid in the same crypto you staked. If you want cash, you’d need to sell the rewards.
Is staking taxable?
In many countries, yes. Staking rewards are treated as income when you receive them, and if you later sell them, there may also be capital gains tax. (Rules differ by country.)





