The day everything changed and the birth of Bitcoin
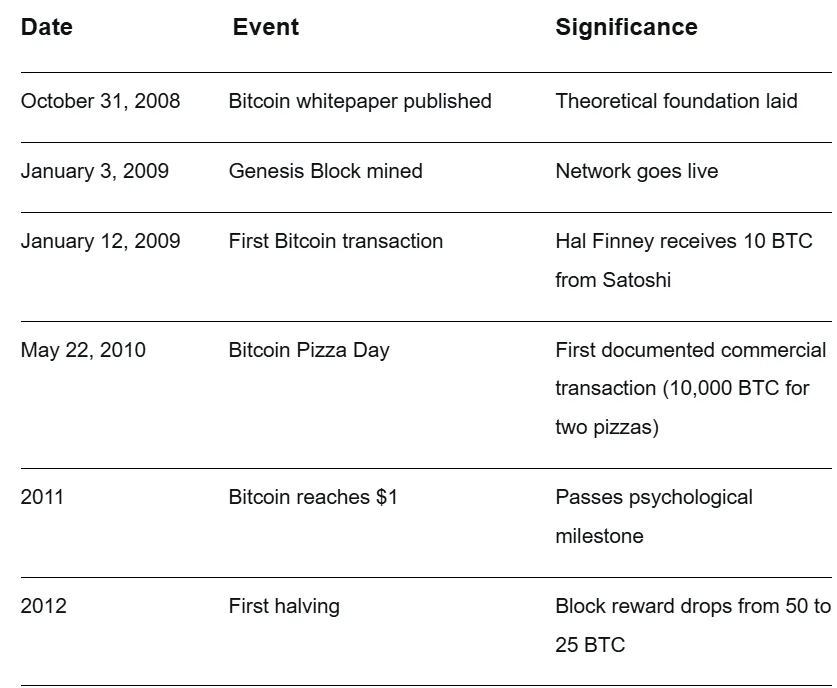
It was January 3, 2009, and the global financial system was in crisis. Banks were failing, governments were preparing massive bailouts, and public trust in financial institutions was crumbling. At this precise moment, someone using the name Satoshi Nakamoto quietly mined the first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, now known as the Genesis Block, setting in motion a revolution that would challenge the very foundations of money and trust.
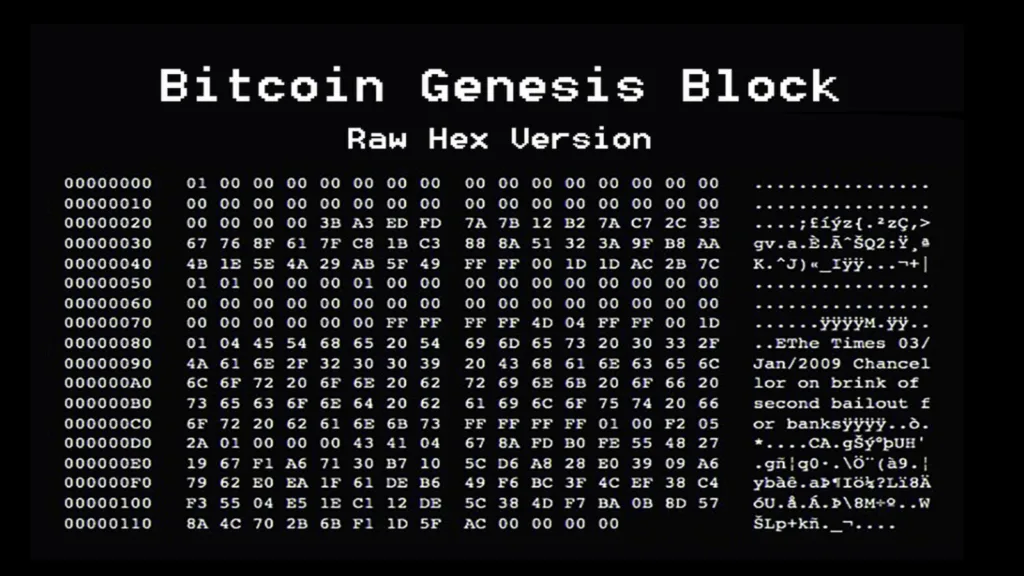
Embedded within this block was a message that would become legendary: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.” This wasn’t merely a timestamp. It was a declaration of intent, a protest against a broken system, and the founding philosophy of what would become a trillion-dollar alternative. The birth of Bitcoin wasn’t announced with press releases or celebrity endorsements; it arrived silently in code, visible to anyone who understood its significance, yet hidden from the world it would eventually transform.
The foundation stone: More than just code
The unspendable foundation
The Genesis Block, block 0, differed from all that would follow in several crucial ways. Most notably, the 50 BTC reward created in this first block is unspendable. This wasn’t an accident. Whether by design or oversight, this foundational bitcoin can never be moved, serving as a permanent monument to Bitcoin’s origins.
Technically, the Genesis Block established the core architecture that would define Bitcoin: proof-of-work mining, a decentralized ledger, and a fixed supply schedule that would systematically reduce new bitcoin creation through events known as “halvings.”
The block’s hash, 000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f, became the cryptographic anchor for everything that followed.
A philosophical blueprint
The embedded Times headline did more than date the block; it explained Bitcoin’s purpose. At a time when central banks were creating billions to bail out financial institutions, Satoshi proposed a system where money couldn’t be inflated at will, where transactions couldn’t be censored, and where no trusted third party stood between users.
This was Bitcoin’s true innovation: it replaced institutional trust with cryptographic verification. The system didn’t care about your identity, your credit score, or your nationality. It only cared about mathematical rules consistently applied and verified by a distributed network of participants.
The early days: Building from obscurity
Mysterious origins
Satoshi Nakamoto’s true identity remains one of technology’s greatest mysteries. We don’t know if Satoshi was a man, woman, group, or organization. What we do know is that they possessed a rare combination of expertise in cryptography, economics, distributed systems, and human psychology.
In early communications with other cryptographers, Satoshi demonstrated both technical brilliance and a pragmatic approach to problem-solving. “I actually did this kind of backwards,” Satoshi told one early collaborator. “I had to write all the code before I could convince myself that I could solve every problem, and then I wrote the paper.”

The first believers
Bitcoin’s earliest adopters weren’t Wall Street institutions but cryptographers, cypherpunks, and idealists who saw beyond the code to its philosophical implications. Hal Finney, a renowned cryptographer, became the first person to receive a bitcoin transaction when Satoshi sent him 10 bitcoins. These pioneers ran the software on their personal computers, discussing improvements in online forums and slowly strengthening the network through participation.
For these early believers, Bitcoin represented something more profound than technology; it offered the promise of financial sovereignty in an era of increasing surveillance and control.
Table: Bitcoin’s Early Historical Milestones
From obscure experiment to global phenomenon
The mining evolution
As Bitcoin grew, so did its security. The early days of laptop mining quickly gave way to specialized hardware called ASICs designed specifically for Bitcoin’s hashing algorithm. The network’s total computational power, its “hash rate,” grew exponentially, making the system increasingly secure against attack.
The mining process itself became Bitcoin’s engine: every ten minutes, on average, miners worldwide compete to solve a mathematical puzzle. The winner adds the next block to the chain and receives newly minted bitcoins as a reward. This process systematically releases new bitcoins according to a predetermined schedule, eliminating human discretion from monetary policy.
The halving mechanism
Built into Bitcoin’s code is one of its most important economic features: the halving. Approximately every four years, the reward for mining new blocks is cut in half. This predictable reduction in new supply creates a systematic deceleration in bitcoin issuance, culminating in a maximum supply of 21 million coins.
The historical halvings occurred in:
- 2012: 50 BTC → 25 BTC
- 2016: 25 BTC → 12.5 BTC
- 2020: 12.5 BTC → 6.25 BTC
- 2024: 6.25 BTC → 3.125 BTC
This predetermined scarcity stands in stark contrast to traditional fiat currencies, which central banks can create in unlimited quantities.

The modern legacy: More than digital gold
Mainstream acceptance
From obscure beginnings, Bitcoin has grown into a global financial asset. Major companies now hold bitcoin on their balance sheets, countries have adopted it as legal tender, and regulated exchanges allow millions to trade it freely. The 2024 approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the United States marked perhaps the most significant step toward mainstream financial acceptance.
Despite this institutional embrace, Bitcoin remains accessible to anyone with an internet connection. This unique combination of global reach and individual accessibility continues to embody its original vision of borderless, permissionless money.
The philosophical legacy
Fifteen years after the Genesis Block, Bitcoin’s most enduring impact may be philosophical rather than technological. It introduced the world to concepts that have since spawned an entire ecosystem of digital assets and blockchain applications.
Yet amidst this innovation, Bitcoin remains unique in its singular focus on being secure, predictable, and decentralized money. While other projects add complexity and features, Bitcoin continues to do what Satoshi designed it to do: provide a neutral, global monetary network controlled by no one and accessible to everyone.
Birth of Bitcoin: The foundation continues
The birth of Bitcoin in that first Genesis Block created more than just a new currency; it introduced a new paradigm for thinking about money, trust, and value. The embedded Times headline continues to remind us of the conditions that made Bitcoin necessary: a world where financial systems remain vulnerable to crises and dependent on institutions that have repeatedly failed the public.
Today, as Bitcoin evolves from rebel protocol to established asset, the Genesis Block remains its moral and technical foundation. Its unspendable reward continues to symbolize that this system wasn’t created for personal enrichment but to offer an alternative to financial fragility.
The quiet revolution that began on January 3, 2009, continues to unfold, one block at a time, offering an increasingly loud reminder that money need not be controlled by the powerful to serve the public. The birth of Bitcoin was just the beginning; the world is still discovering what it makes possible.





